いま、1型糖尿病は
2008年03月07日
33Time Required for Blood Glucose to Fall Following Insulin Injection

As I see outpatients, I have realized that many patients believe insulin works immediately after it is injected.
In this article, let us think how insulin administered under the skin at a certain location starts working throughout the body.
Naturally, the time required for short-acting insulin to act is as short as about five minutes.
In this article, I am going to touch on regular or short-acting insulin.
Is insulin in insulin formulation human insulin?
Is insulin in regular insulin product the same as human insulin? You may have never thought about it, but the answer is yes. It is the same as human insulin.
However, while human insulin exists as a single molecule in the blood, insulin in insulin formulation contained in a vial, cartridge or pen is a complex of six molecules even though it is human insulin product. It is because insulin molecules become stable when six molecules assemble together. This complex of six molecules is called a hexamer. And when a molecule exists as a single molecule, it is called a monomer.
What about human insulin in secretory granule right before its secretion by pancreatic beta cells? It is a hexamer.
Short-acting insulin is not human insulin, but it is formulation in the form of hexamers. Regular and short-acting insulin could be considered the same in that both are insulin products with six molecules assembled together.
What will happen when regular insulin is injected under the skin?
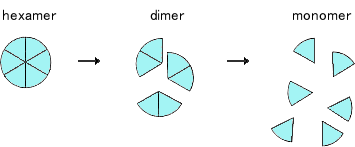
Regular insulin in the form of hexamers, when injected under the skin, becomes diluted in "intercellular fluid" that exists between cells. When insulin formulation of "1mL=100 units" is diluted more than ten thousandfold, hexamers start turning into dimers and then into monomers, that is a single molecule. Insulin concentration in insulin products is approximately 100,000 to 10 million times (105〜107times) more than that in the blood. Once insulin becomes dimers or monomers, they can enter into the blood vessels. Insulin in the form of monomers gradually penetrates into capillary blood under the skin.
Then insulin gradually flows through large blood vessels, from great veins via the heart to every peripheral vessel throughout the body, reaching every cell of the entire body. It is only after insulin enters cells that insulin action, lowering blood glucose, occurs.
In the case of regular insulin, it takes about 30 minutes for insulin action to occur.
What will happen when short-acting insulin is injected under the skin?
Short-acting insulin needs shorter time in the process from hexamers turning into monomers, and it is not the same as human insulin. It is "mock human insulin" meaning that it is similar to human insulin but it is not similar to human insulin in some ways.
Humalog? that became available at the end of August 2001 in Japan is insulin formulation in the form of hexamers. When diluted, it turns straight into monomers instead of dimers, and thus it requires shorter time to enter capillary blood vessels.
Rapid? became available in December 2001 in Japan. Although it is an insulin product, it contains mock hexamer insulin and turns into monomers immediately after diluted. Because of that nature, it can easily enter capillary vessels.
When regular insulin is injected intravenously
If you have a sick day and go to a hospital, you will have your blood glucose, urine or blood ketone body measured. You are obviously hyperglycemic and need to lower blood glucose fast.
In such a case, insulin is injected directly into blood vessels. In most cases, regular insulin with 10mL or 100 mL of physiological saline solution added is administered by constant intravenous infusion.
When insulin is injected directly into the vein, it turns immediately into monomers. Therefore, insulin action takes place immediately.
Insulin does not "take effect" immediately after injection
You now understand that insulin does not work throughout the body immediately following an injection. It goes through every step before it reaches the entire body and starts taking effect.
©2008 Yasuko Uchigata
インスリン注射してから血糖が下がるまで

外来をしていますと、注射したらすぐインスリンの作用が現れると思っている方が多いことに気がつきました。
皮下のある一部にインスリン注射をして、その後どのようにしてインスリン作用がからだ全体に現れるのか、一度考えてみましょう。
もちろん、超速効型インスリンは、この過程にかかる時間が5分くらいといわれるように、短いわけですね。
今回は、速効型ないし超速効型インスリンの話です。
ただし、ヒトインスリンは血中では1分子として存在しますが、インスリン製剤としてバイアル瓶やカートリッジやペンの中に入っているインスリンは、ヒト型インスリン製剤であっても、6分子がひとつのかたまりとなって入っています。インスリン分子は6分子が集まると安定するためです。これを6量体といいます。1分子として存在するものを単量体といいます。
膵臓のβ細胞の、インスリン分泌寸前の分泌顆粒中にあるヒトインスリンは何量体でしょうか。6量体です。
超速効型インスリンはヒトインスリンではありませんが、やはり6量体の製剤になっています。6つの分子が集まって製剤になっているという点では、速効型インスリンも超速効型インスリンも同じといえます。
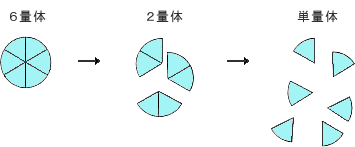
そうして、だんだん大きな血管へ流れていき、大静脈から心臓を経由して、大動脈から今度は全身の末梢の細かい血管のすみずみまで流れていき、全身の1個1個の細胞にインスリンが届くというわけです。インスリンが細胞の中に入って、はじめてインスリンの作用、つまり血糖が下がるということが発現します。
このような過程に、速効型インスリンならば、約30分前後かかるというわけです。
2001年8月末に日本で使用できるようになったヒューマログ®は、製剤中では6量体ですが、希釈されると、2量体にはなりにくく、すぐ単量体になってしまう性質をもつインスリン製剤です。よって、毛細血管に入りこむまでの時間が短くなります。
次に2001年12月に日本で使用できるようになったラピッド®は、もともと製剤でも6量体になりにくくやっとやっと6量体もどきになっているというインスリン製剤で、皮下に入って希釈されるとすぐ単量体になってしまいます。そのために、毛細血管に容易に入り込みやすくなっています。
このような場合には血管の中に直接インスリンを入れます。通常は速効型インスリンを、100mLや10mLの生理的食塩水に、加えて持続的に静脈中にいれます。
皮下から入れるのではなくて、直接静脈の中に入れますと、インスリンはただちに単量体になってしまいます。そして、インスリン作用がただちに発揮されるというわけです。
※ヘモグロビンA1c(HbA1c)等の表記は記事の公開時期の値を表示しています。
Copyright ©1996-2024 soshinsha. 掲載記事・図表の無断転用を禁じます。
治療や療養についてかかりつけの医師や医療スタッフにご相談ください。

 医療・健康情報グループ検索
医療・健康情報グループ検索